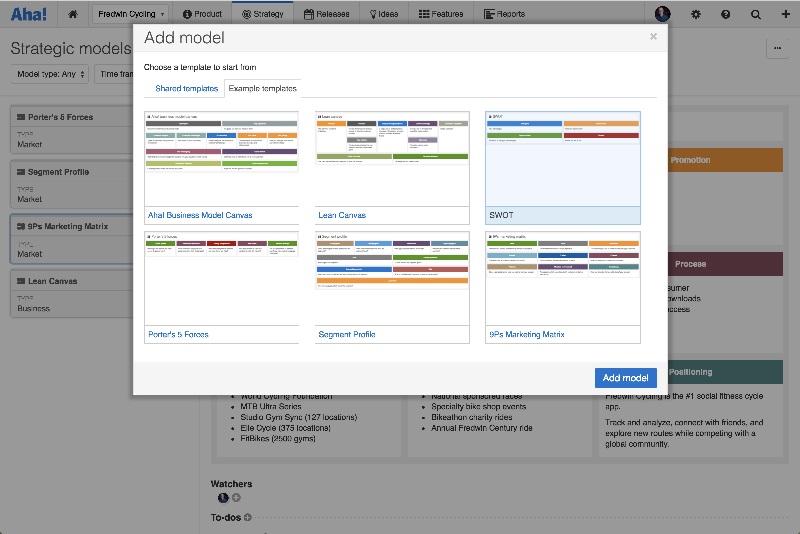
Today I am sharing a breakdown of the CIRCLES Problem Solving and RICE Prioritization Frameworks and how to approach a problem in a thoughtful, methodical, and analytical way. I find this handy to follow along as I am working on a problem to ensure every step is taken with intention and meaning.
I like to think that other people would like to use this information as well so I figured I should share it with you all. Feel free to add me on LinkedIn and show some endorsement <3 if you like the information!
CIRCLES Problem Solving & RICE Prioritization Method – Design Thinking Framework
By Matthew Knoot
How to answer the question, “What feature/product would you build and why?”
Comprehend the Situation
- What is the product?
- Who is it for?
- Why do they need it?
- How does it work?
Identify the Customer
- What are the User Personas?
- Examples – Hungry guests, guests looking for parking prior to arrival, lost guests looking for their group.
Report the Customer’s Needs
- As a <user type> , I want to <perform some action> so that I <can achieve some goal/result/benefit>.
- Example – As a hungry theme-park guest, I want to find places to eat so that I can satisfy my hunger cravings quickly.
Cut, through Prioritization
- “I am going to do a Return On Investment (ROI) estimate using the RICE method.”
- [R * I * C] / E Prioritization Method
- [14 million * 50% * 75%] / 10 = 525,000 RICE Score <== Result can only be used compare with other options calculated with same types of values.
- Reach – How many customers will this feature impact (Google the market size)? (Specific user group size?).
- 14 million – assuming 75% of our annual visitors.
- Impact – How thoroughly will this feature solve our customer’s problem? (What alternative existing products or services might exist? Will it fulfill 80/20 rule solving 80% of the problem?)
- 50% (alternative is the in-park printed map).
- Confidence – How confident am I in my estimates of Reach and Impact?
- 75%.
- Effort – How much work/time/cost is this going to take?
- 10 Sprints – would need to ask Engineering team for realistic answer, can also answer in Fibonacci Sequence value for individual feature/user story [1, 2, 3, 5, 8].
- Drawback to RICE method is having to group a diverse (higher/lower value) user base into one sum. Ideally it’s valuable for considering similarly valued groups of customers.
List Solutions
- Reversal Method – reverse the situation to uncover new solutions.
- Example: Help hungry guests find a place to eat quickly.
- Need: Hungry guests may not even know where they are.
- Solution based on reversal method: The app should locate the user and display pins with nearby food facilities with details like wait time, type of food, and relative cost.
- Why Method – challenge the status quo.
- Example: Help hungry guests find a place to eat quickly
- Need: Why do guests need to go to a food facility? Why aren’t the food facilities mobile?
- Solution based on why method: The theme-park can field a fleet of mobile food trucks or carts within the park.
Evaluate trade-offs
- Be thoughtful, analytical, and objective.
- Define your potential Trade-off Criteria (KPI’s) like cost, time, benefit, user satisfaction etc.
- Make a grid and score each Trade-off Criteria (KPI) then total scores and compare.
- Try a pro and con list for each potential solution, maintain neutrality do not get defensive .
Summarize Recommendation
- What – Tell the interviewer/stakeholder which product or feature you recommend
- Recap – Review why the solution is beneficial to the user/customer and/or the company.
- Why vs. Others – Explain again quickly why this solution won in the Evaluate phase.
Here is a list of some popular Metrics tools you might want to try (no affiliation): Google Analytics, Crazy Egg, KISS Metrics, Mixpanel, Optimizely (also AB Testing), Segment, Adobe Analytics.
Check out my other articles!
Join the discussion: https://www.reddit.com/r/ProductManagement/
“Thank you for reading and good luck building that next Rockstar Product!” –Matthew Knoot